The beauty of enterprise risk management (ERM) is that every one of the discipline’s constituent parts is interrelated.
Connected at the hip.
Nothing in ERM appears “out of the blue”, therefore.
Last month, for instance, we told you that a robust and meaningful ERM program might consider adopting a concise ERM mission statement, one that ties together the “what” and “why” of ERM something like this:
“Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is the process to identify, assess, mitigate and monitor all enterprise-wide risks that might impair the company’s ability to achieve its strategic business objectives.”
In short, we offered the opinion that an ERM mission statement could help underline the fact that the achievement of strategic business objectives depends upon the four step process involved in the tactical execution of risk.
That four step process – identify, assess, mitigate and monitor – is performed over and over again, on an iterative basis.
Now, seamlessly, we move onto our views on ERM reporting.
Specifically, it is our opinion that, in order to monitor the ongoing success of that centerpiece ERM mission statement, it is incumbent upon an ERM program to develop a powerful ERM reporting regimen that is built upon the following five (5) pillars:
- Link ERM Reporting to an Embedded and Fully-Integrated Risk Register
- Champion ERM Governance and Accountability
- Insist upon Transparency and Clarity in ERM Reporting
- Promote Risk Culture throughout ERM Program and Reporting
- Demand High Quality Reporting for All Stakeholders
A more complete explanation of those five (5) pillars:
- Link ERM Reporting to an Embedded and Fully-Integrated Risk Register
- Avoid: garbage in, garbage out.
- By contrast, aspire to: quality in, quality out.
- Risk reports will only be as good as the efforts devoted to the thankless, hard work involved in compiling and maintaining the underlying risk register.
- Reports need to link up with, and flow directly and automatically out of, a company’s fully-operational and totally-embedded risk register.
- There is no mystery to this: in ERM, everything needs to works together, in lockstep.
- There are no risk universe gaps that are acceptable.
- The universe of risks needs to be arrived at after systematic categorization and careful identification of all possible risks.
- Nothing less than 100% commitment to the discipline of ERM, as well as full adherence to an overall enterprise risk register system, will work.
2. Champion ERM Governance and Accountability
- What is the key ERM governance shortcoming that a company should be trying to avert?
- Simply put: failure to assign responsibility to the appropriate Risk Owner(s).
- All it takes is one critical risk to be overlooked.
- Most recent egregious example of ERM Governance malfeasance – Silicon Valley Bank (SVB)
- In that case, the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) position for SVB was left unfilled for an unconscionable eight (8) months.
- How can something not go wrong with such gross malpractice?
- ERM Governance Step #1: Establish Risk Manager or CRO as person in charge of overall ERM program and responsible for risk universe oversight.
- ERM Governance Step #2: Assign one Risk Owner for each risk in the universe – operative precept for this is “Buck Stops Here”.
- ERM Governance Step #3: Demonstrate the proven, embedded nature of ERM by detailing the Three (3) Lines of Defense responsibility for each individual risk control.
3. Insist upon Transparency and Clarity in ERM Reporting
- Bottom line: what good is reporting if nobody understands the particulars?
- Risk Owner Report “tells the ERM story” in a logical and sequential manner: chronicling causes, consequences, controls and key risk indicators (KRIs) for each risk.
- Word format for that Risk Owner report allows risk owners to update “story line” as needed.
- With story in place, Risk Owner can then move on and properly rate metrics for each risk (severity, likelihood, direction and velocity).
- “Pop-ups” should be provided in the ERM tool in order to make rating process understandable, transparent and consistent, across the universe.
- Ratings need to be straightforward and intuitive, especially since Risk Owners may have no background in ERM but are still deputized to be Risk Owner once a year.
- Key point: don’t make this an academic, hypothetical or open-to-debate exercise.
- “Just do it”.
- Prioritization of risks will follow automatically, based upon ratings.
- Ratings will point company to best use of resources and time, around the subject of risk.
Comprehensive Risk Report

4. Promote Risk Culture throughout ERM Program and Reporting
- Definition: shared understanding and behavioral attitudes of the company’s employees towards risk-taking.
- Answers the question: “Is everyone on the same page with regard to risk management?”
- Undeniable fact: no place to hide when there is a cogent reporting mechanism in place.
- Responsibly and teamwork is demanded of everyone.
- Everyone needs to understand what’s at stake (satisfying ERM mission statement) and what’s to lose if tactical execution of ERM does not lead to strategic business objectives being met.
- Logical extension: link remuneration, at least in part, to the successful management of risk.
5. High Quality Reporting for All Stakeholders
- Simultaneously satisfies internal (Board) and external (Regulatory) reporting requirements.
- Different constituencies have their own unique reporting needs.
- Risk arrow heat map indicates both inherent and residual risk values for each risk and demonstrates the impact of (and reliance upon) controls.
- Ideal situation is one where there is a fully-embedded ERM platform able to handle all of reporting needs without downloading reports into a separate tool, like Power BI.
- Effective reporting leads to actionability around risk tolerances and appetite.
Risk Scorecard – Cyber Security
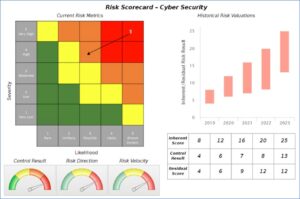
Very simply, the engine that drives powerful and impactful ERM reporting is the risk register.
ERM One™ is a revolutionary, yet straightforward, risk register application that DoubleCheck LLC has developed, based upon what it has been privileged to learn from clients over time.
It is an out-of-the-box tool that delivers an integrated ERM process together with a comprehensive, high-level categorization of exposures (Financial, Core Business, Operational and Strategic), fully loaded with over 60 pre-populated risks to be used as a starting point for the risk register.
ERM One™ incorporates into one, intuitive turn-key risk register product the best-practices tools and content to help optimize ERM and thereby put your firm on a path to achieving its strategic business objectives.
Click HERE to download a FREE copy of our ERM One™ white paper.
About the Author:
Michael Cawley is a risk management executive with a 35-year record of broad and diversified accomplishment in the strategic and tactical elements of corporate enterprise risk management (ERM). He performed day-to-day development and execution of a risk management program that covered all elements in the identification, assessment, mitigation and monitoring of all exposures within the corporate risk universe. Specific experience involved being a corporate risk manager for a service-related conglomerate (15 years) and then a biopharmaceutical manufacturer (10 years) before assuming an ERM governance and disclosure leadership role (10 years, through 2021) for a major worldwide financial entity. Currently, Mike serves as a Subject Matter Expert (SME) in an advisory role for ERM Best Practices for the advancement of DoubleCheck’s new ERM One™ application.

